Review of Bitumen in Road Construction
Bitumen Road Construction, also known as asphalt, is a versatile and essential material in various industries, primarily in road construction applications. Derived from crude oil, bitumen is a black, sticky, and highly viscous substance that has been used for thousands of years.
The most widespread use of bitumen is in road construction, where it is used as a binder mixed with aggregate to create asphalt concrete. This application accounts for about 85% of bitumen consumption globally.
why is Bitumen Important in Road Construction?
The First Reason Bitumen, a powerful adhesive, forms asphalt concrete by binding aggregates, ensuring a stable, durable road surface that withstands traffic loads and environmental stresses. Also, Roads made with bitumen are capable of withstanding heavy traffic and severe weather conditions for extended periods, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing safety.
The another reason Bitumen, a versatile material, exhibits remarkable flexibility, allowing it to adapt to temperature changes without cracking. Its ability to soften slightly in hot climates and resist brittleness in colder conditions makes it suitable for various regions. Also, Bitumen-based pavements offer efficient road construction due to their quick and easy installation and repair processes, facilitated by the on-site heating and mixing of bitumen with aggregates.
Types of Bitumen in Road Construction
Bitumen is classified into several types based on its source, refining process, properties, and intended use. Each type has specific characteristics that make it suitable for different applications, particularly in road construction.
Here are the main types of bitumen in Road Construction:
- Bitumen Penetration
- Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB)
- Viscosity Grade Bitumen (VG)
- Cutback Bitumen
- Bitumen Emulsion
1. Bitumen Penetration in Road Construction
Penetration grade bitumen is the most common type used in road construction. It is classified based on its hardness or softness, which is determined by the depth a standard needle penetrates the bitumen sample under specific conditions (temperature, weight, and time). This grade indicates how bitumen will perform under various climatic conditions.
Bitumen (asphalt) penetration is widely used as a binder in asphalt mixes for road construction. It provides the necessary adhesive properties to bind aggregates, creating a durable and flexible road surface.
Grades of Bitumen Penetration
- Bitumen 60/70
- Bitumen 80/100
- Bitumen 40/50
- Bitumen 200/300
2. Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB) in Road Construction
Polymer-Modified Bitumen (PMB) is a specialized type of bitumen enhanced with polymers, enhancing its performance characteristics, particularly in road construction, particularly in heavy traffic areas. The use of PMB has gained popularity due to its superior durability, flexibility, and resistance to deformation, which contribute to longer-lasting and safer roads.
The choice of polymer and its concentration in the bitumen depends on the specific requirements of the road construction project.
Grades of PMB
- PMB 10/40-70
- PMB 25/55-65
- PMB 45/80-60
- PMB 75/130-60
3. Viscosity Grade Bitumen (VG) in Road Construction
Viscosity grade bitumen is classified based on its viscosity at a standard temperature (usually 60°C) and is used mainly in countries like India. The viscosity test determines how the bitumen will behave in the mixing and compaction stages during road construction.
Grades of VG Bitumen
- VG-10
- VG-20
- VG-30
- VG-40
4. Cutback Bitumen in Road Construction
Cutback bitumen is a form of bitumen whose viscosity has been reduced by adding a solvent such as kerosene or diesel, making it easier to work with at lower temperatures. It is often used in road maintenance and repairs, particularly in surface dressing and patching.
The Main Grades of Cutback Bitumen
- Rapid-Curing (RC)
- Medium-Curing (MC)
- Slow-Curing (SC)
5. Bitumen Emulsion
Bitumen emulsion is a mixture of bitumen and water stabilized by an emulsifying agent, making it a liquid at ambient temperatures.
The Main Grades of Bitumen Emulsion
- Cationic Bitumen Emulsion
- Anionic Bitumen Emulsion
The Structures of Road Construction
The structures of Road vary based on factors like traffic volume, environmental conditions, and the road’s intended use. The knowledge of road construction structure can help to understand what bitumen could be used for better performance of road construction.We are explaining from the high layer to the low layer, and continuing with what kind of bitumen should be used in each layer.
Here is a breakdown of the primary structures involved in road construction:
- Surface Course
- Binder Course
- Base Course
- Sub Base Course
- Sub Grade
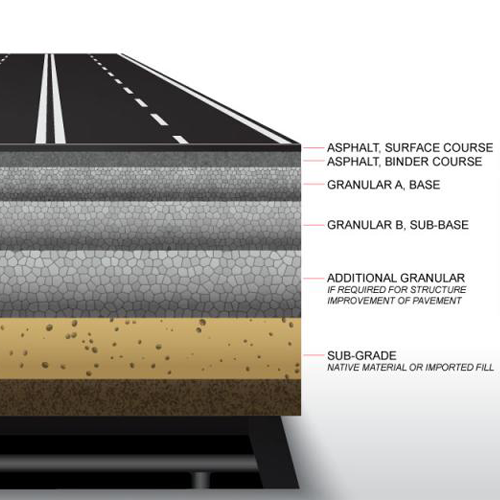
1. Surface Course
The topmost layer of the road pavement directly exposed to traffic is called wearing course or surfacing. It may consist of one or more layers in case of flexible pavements. A good Surface course should be designed based on anticipated traffic loads, climate, and also bundled with thickness, texture, and quality.
Suggest Bitumen
for this layer can be uses of Cold Bitumen and Hot Bitumen.
- Hot Bitumen (Bitumen penetration): Bitumen 60/70 , Bitumen 80/100, Bitumen 40/50, Bitumen 200/300
- Cold Bitumen (Cutback Bitumen & Bitumen Emulsion): RC-70, RC 250, MC-30, MC-250, SC-70, CSS-1, CSS-1h
2. Binder Course
Binder course is placed between the surface course and base course. It prevents the surface course from moving and shifting. Binder Course’s hot asphalt consists of coarse aggregates and bitumen. Its bitumen content is less than the bitumen in surface course asphalt. It carries part of the load the surface has to deal with and also helps to waterproof lower layers.
Suggest Bitumen
- Bitumen penetration: 60/70, 80/100, 120/150, 200/300
- Viscosity Grade Bitumen (VG) : VG-10, VG-20, VG-30, VG-40
3. Base Course
This Layer placed under the Binder Course, It provides additional load distribution and contributes to drainage. the Base Course can be transfer of pressure from surface course to base course.It is made of granular materials like crushed stone, gravel, or sand, designed to withstand traffic weight.
The base course’s thickness and composition vary based on traffic volume, soil conditions, and climate.A well-constructed base course ensures pavement durability, distributes loads evenly, resists deformation, and provides adequate drainage.
4. Sub Base Course
The sub-base course, often referred to as the sub-grade, forms the foundation upon which the base course and pavement layers are constructed.
5. Sub-Grade Course
This layer is a important layer Because all of the layers placed on it. The Sub-Grade Course should be Strong.
What is Tack Coat?
Tack coat is a thin adhesive material applied between layers of asphalt pavement, creating a strong bond to enhance road durability and longevity. It is crucial in road construction and maintenance, particularly in new road construction and rehabilitation. This layer usually placed between Surface course and binder Course.
Tack coat ensures even load stresses transfer between layers, preventing delamination or separation from shear forces. This bonding process maintains a smooth, stable road surface, contributing to safety and comfort for road users.
Tack Coat Materials
There are several types of materials used for tack coats, The most commonly used materials include:
- Bitumen Emulsion (Cold Bitumen): CRS-1, CRS-2, CSS-1, CSS-1h
- Cutback Bitumen (Cold Bitumen): MC-30, MC-70
Prime Coat Usage
A prime coat is a protective layer that binds loose particles on the base course surface, seals it against water penetration, and enhances adhesion between the base course and overlaying layers. It acts as a waterproofing agent, controlling dust and creating a cleaner work environment, especially in dry or windy conditions. This enhanced bond contributes to the road’s longevity and performance, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and repairs.
Prime Coat Materials
- Bitumen Emulsion (Cold Bitumen): All Grades of Anionic Bitumen and Cationic Bitumen
- Cutback Bitumen (Cold Bitumen): RC-70, RC 250, MC-30, MC-250, SC-70


